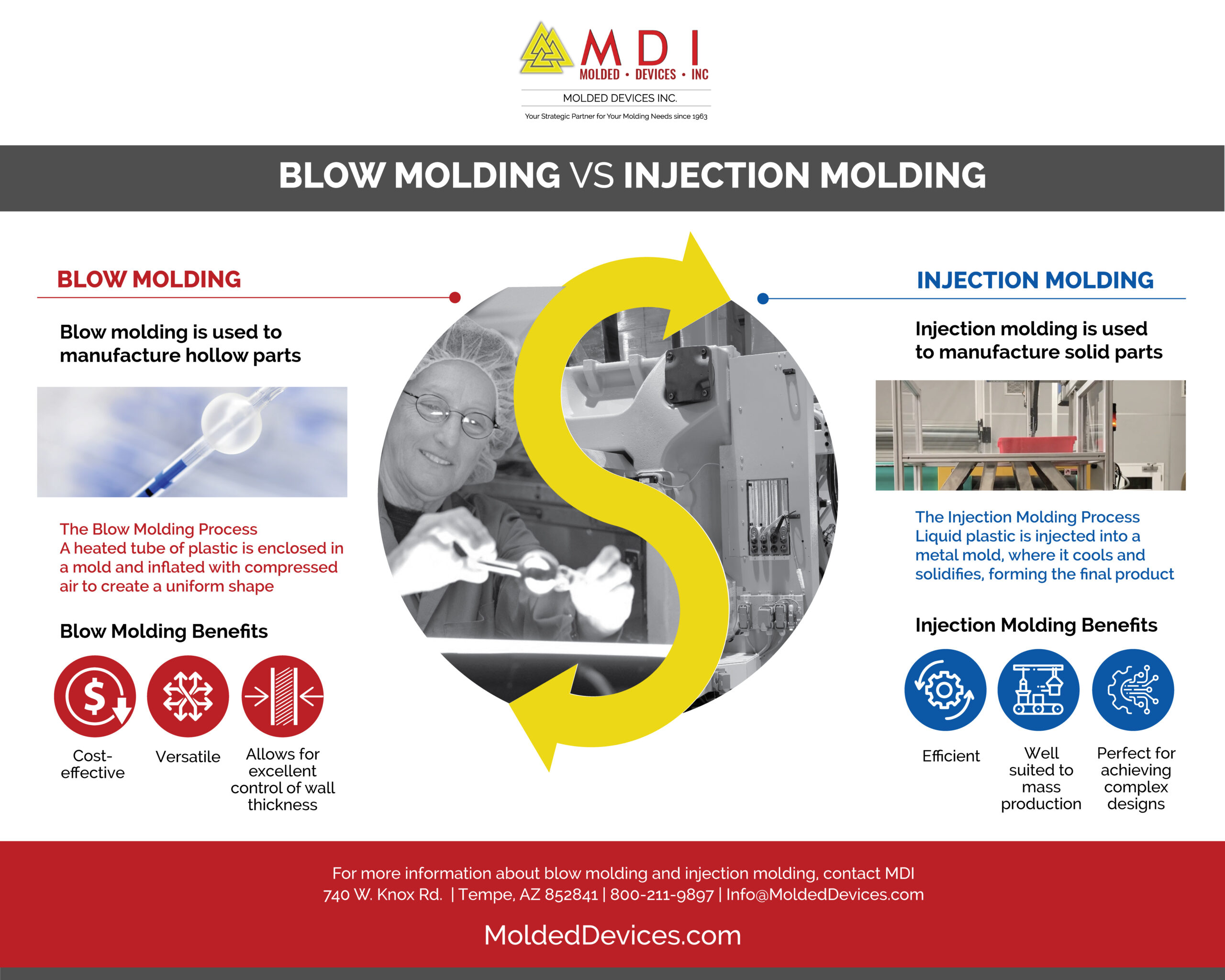
What is the difference between injection blow molding and extrusion blow molding?
Answer: Extrusion blow molding blows compressed air into molten plastic to make it expand into a formed mold and is used only to make hollow parts with little surface detail, such as bottles and jugs. Injection molding injects molten plastic into a mold and is used to make primarily solid parts with high degrees of intricacy.
Extrusion blow molding:
Between both methods, the extrusion blow molding method tends to be the more popular choice. Plastic pellets are fed from a hopper into an extruder, which uses friction to heat the plastic into a liquified state. The molten plastic is extruded into a hollow tube, called a parison. Pressurized air is then blown into the parison, forming it into shape. Excess plastic on the bottom of the container is trimmed. Containers are then sent to a second trimming station, where the top is trimmed. When possible, this excess is recycled back through the process to limit waste.

Injection molding:
Injection molding creates greater detail than extrusion blow molding. Resin pellets are fed from a hopper into an extruder. The pellets are then melted and injected into a preform mold around a core rod. Pressurized air forces the plastic to take the shape of the mold.
The final step in both blow molding processes is to check for leaks. If a leak is detected the container is recycled back into production to limit waste. MDI offers both extrusion and injection blow molding services, with extensive custom capabilities.
HAVE A QUESTION?
WE ARE HERE TO HELP!

